Architecture
Apr 8, 2021
Nebula Spark Connector Writer: Implementation and Practices
Nicole Wang
In "Nebula Spark Connector Reader: Implementation and Practices", it is known that Nebula Spark Connector is a connector for Spark reading data from or writing data into NebulaGraph. It is composed of Reader and Writer. In this article, I will introduce how Nebula Spark Connector makes writing data from other data sources into NebulaGraph possible.
How Nebula Spark Connector Writer is Implemented
Spark SQL supports customizing data sources, making Spark integrating with third-party data sources possible.
Writing a single record into NebulaGraph with Nebula Spark Connector is implemented based on DatasourceV2. Here is how it is implemented:
The
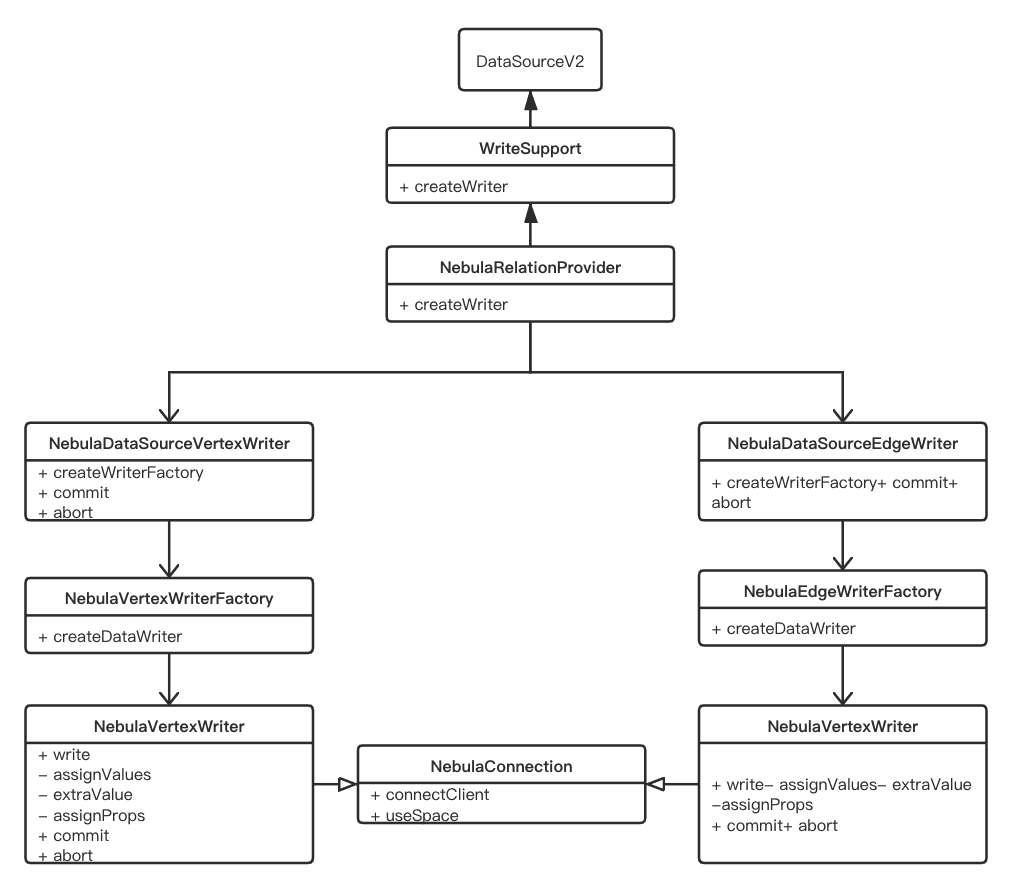
WriteSupportinterface is inherited and a newcreateWritermethod is defined to create a customDataSourceWriter.The
DataSourceWriterinterface is inherited and theNebulaDataSourceVertexWriterclass and theNebulaDataSourceEdgeWriterclass are created. A newcreateWriterFactorymethod is defined and a customDataWriterFactoryis returned. A newcommitmethod is created to commit the entire transaction. A new abort method is defined for transaction rollback. Please note that NebulaGraph 1.x does not support transactions, so thecommitandabortmethods in this implementation will not be actually called.The
DataWriterFactoryis inherited and theNebulaVertexWriterclass and theNebulaEdgeWriterclass are created. ThecreateWritermethod is defined and a customDataWriteris returned.The
DataWriterinterface is inherited and theNebulaVertexWriterclass and theNebulaEdgeWriterclass are created. A newwritemethod is defined to write data out. A newcommitmethod is created to commit the entire transaction. A newabortmethod is defined for transaction rollback. Please note that NebulaGraph 1.x does not support transactions, so thecommitandabortmethods inDataWriterwill not be actually called.
The class diagram of the implementation of Nebula Spark Connector Writer is as follows.
How to write a single record into NebulaGraph is implemented in the write method in NebulaVertexWriter and NebulaEdgeWriter:
Creates a client and connects it to the Graph Service of NebulaGraph.
Specifies a graph space to write data into.
Constructs nGQL statements to insert data into NebulaGraph.
Commits the nGQL statements and executes them.
Defines callback functions to receive the execution results.
Nebula Spark Connector Writer batch writes data into NebulaGraph via cumulative commits of batch data transformed by the mapoperation on DataFrame, which is similar to the implementation of Nebula Exchange.
Practices of Nebula Spark Connector Writer
Nebula Spark Connector Writer provides users with two interfaces to program to write data into a third-party data source. The source of the data is DataFrame. Nebula Spark Connector Writer provides two types of interfaces to write single records and write data in batches.
Run these commands line by line to pull the source code of Nebula Spark Connector from GitHub and compile Nebula Spark Connector. Then, copy the package to the local Maven repository.
Here is an example to introduce how to use Nebula Spark Connector Writer.
Add the
nebula-sparkdependency into the POM file of your Maven project.
The Spark application uses an interface of Nebula Spark Connector Writer to write data of DataFrame into NebulaGraph.
2.1 Writes a single record into NebulaGraph:
Explanation of the parameters:
nebula(address: String, space: String, partitionNum: String)
address:Specifies the Graph server addresses and their ports. Multiple addresses are supported. The addresses must be separated with commas. The default port is 3699. For example, "ip1:3699,ip2:3699".
space: Specifies the graph space name of NebulaGraph.
partitionNum:Sets to the value of partitionNum that was specified during the creation of the graph space. If no value was specified, the default value
100is used.
writeVertices(tag: String, vertexFiled: String, policy: String = "")
tag:Sets to a tag name created in the graph space.
vertexFiled:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the vertex IDs. For example, if the DataFrame is composed of three columns, a, b, and c, and column a is used as the source of the vertex IDs, then set this parameter to a.
policy:If data of the
vertexFieldcolumn is not of aninttype, a mapping policy is necessary and set policy to "hash". Otherwise, leave it blank.
writeEdges(edge: String, srcVertexField: String, dstVertexField: String, policy: String = "")
edge:Sets to an edge type name created in the graph space.
srcVertexField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the source vertex ID of an edge.
dstVertexField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the destination vertex ID of an edge.
policy:If data of the
srcVertexFieldcolumn and/or thedstVertexFieldcolumn is not of aninttype, a mapping policy is necessary and set policy to "hash". Otherwise, leave them blank.
2.2 Batch writes data to NebulaGraph
Explanation of the parameters:
batchInsert(address: String, space: String, batch: Int = 2000)
address:Specifies the Graph server addresses and their ports. Multiple addresses are supported. The addresses must be separated with commas. The default port is 3699. For example, "ip1:3699,ip2:3699".
space:Specifies the graph space name of NebulaGraph.
batch:Sets to the number of records to be written into NebulaGraph in one batch. Optional. The default value is 2000 .
batchToNebulaVertex(data: DataFrame, tag: String, vertexField: String, policy: String = "")
data:Sets to the DataFrame to be written into NebulaGraph.
tag:Sets to a tag name created in the graph space.
vertexField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the vertex IDs.
policy:If data of the
vertexFieldcolumn is not of aninttype, a mapping policy is necessary and set policy to "hash". Otherwise, leave it blank.
batchToNebulaEdge(data: DataFrame, edge: String, srcVertexField: String, dstVertexField: String, rankField: String = "", policy: String = "")
data:Sets to the DataFrame to be written into NebulaGraph.
edge:Sets to an edge type name created in the graph space.
srcVertexField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the source vertex ID of an edge.
dstVertexField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the destination vertex ID of an edge.
rankField:Specifies a column of the DataFrame as the source of the rank value of an edge. Optional.
policy:If data of the
srcVertexFieldcolumn and/or thedstVertexFieldcolumn is not of aninttype, a mapping policy is necessary and set policy to "hash". Otherwise, leave them blank.
So far, the introduction to Nebula Spark Connector Writer is done. You are welcome to pull the source code from the GitHub repository (https://github.com/vesoft-inc/nebula-java/tree/v1.0/tools/nebula-spark) and try it out.
If you encounter any problems during the trial, please feel free to ask questions and discuss in under the nebula-spark-connector repository.

Go From Zero to Graph in Minutes
Spin Up Your NebulaGraph Cluster Instantly!