ToolsLLMNews
Announcing the Open-Source Release of NebulaGraph MCP Server: Exploring the Infinite Possibilities of AI + Graph Databases
Over the past few weeks, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) has sparked widespread discussion and attention within the technical community. Inspired by this momentum, I have contributed to several related open-source projects, including implementing McpToolSpec for the official LlamaIndex repository and collaborating with Xuanwo and FrostMing to develop a Model Context Protocol Server for Apache OpenDAL™.
As the only protocol currently offering a significant ecosystem advantage, MCP presents an exciting opportunity. In this context, we have implemented a simple NebulaGraph MCP Server based on NebulaGraph 3.x. This marks the first foundational component in the NebulaGraph X MCP ecosystem, opening up new avenues for exploring the potential of combining AI with graph databases.
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
MCP, introduced by the Anthropic team, is an open protocol designed to provide AI systems with a unified and efficient way to access diverse data resources. By adopting a client-server architecture, MCP standardizes data access, addressing the fragmentation issues that traditional AI systems face when interacting with various data sources.
Key Features of MCP:
- Standardized Communication: MCP enables AI assistants to seamlessly access a wide range of data sources, including local data, remote services, and enterprise tools.
- Openness and Ecosystem Advantage: The MCP community already boasts nearly 1,000 MCP Server implementations, spanning search engines, weather services, databases, and more, facilitating rapid tool integration.
- Flexible Architecture: By defining clear interaction protocols between clients and servers, MCP empowers developers to build scalable and reusable systems.
While challenges around security and reliability remain, these issues are expected to be addressed as the protocol evolves and matures with improved development practices.
Features of NebulaGraph MCP Server
Given my recent focus on Graph RAG and Agentic Workflow, leveraging large language models (LLMs) and intelligent agents to uncover insights from graph data has become a critical area of exploration. To facilitate this, I quickly developed the NebulaGraph MCP Server, enabling NebulaGraph 3.x to integrate into the MCP ecosystem as a tool for LLMs like Claude and GPT to invoke and utilize.
Built on FastMCP , the NebulaGraph MCP Server adheres to the core specifications of MCP, providing a lightweight and efficient connection service for graph databases. By exposing NebulaGraph's capabilities through standardized tool interfaces, this server allows LLMs to effortlessly interact with NebulaGraph data for basic graph exploration tasks.
Multiple Transmission Modes:
- Supports both stdio and SSE (Server-Sent Events) transmission modes, catering to diverse development and deployment scenarios.
Basic Graph Exploration Capabilities:
- Graph Space Listing: Enables models to query available graph spaces.
- Schema Querying: Supports querying schema definitions for specified graph spaces.
- Query Execution: Facilitates executing NebulaGraph queries via the MCP Server.
Built-in Operator Templates:
- Includes templates for common operations like pathfinding and neighbor discovery, allowing LLMs to quickly retrieve preliminary insights from graph data.
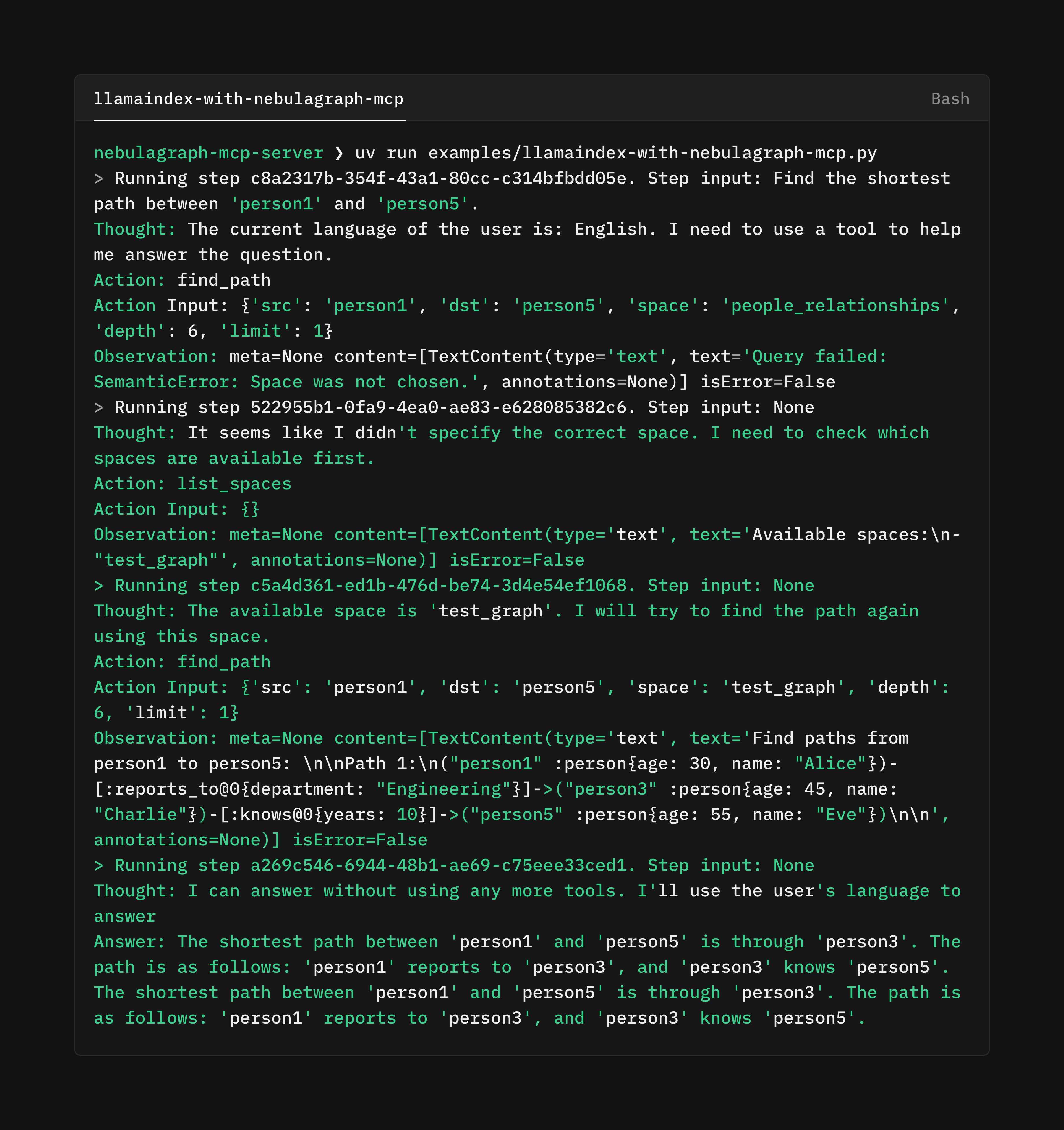
To demonstrate its functionality, I built a simple example using McpToolSpec from LlamaIndex and ReActAgent. Below is a screenshot showcasing its capabilities:
Conclusion
The NebulaGraph MCP Server represents an initial step in contributing to the MCP ecosystem, aiming to bridge the gap between language models and graph databases. As the protocol matures and its ecosystem expands, we hope it can play a vital role in real-world applications. If you're interested in this direction, we invite you to explore, experiment, and collaborate with us!
Together, let’s unlock the full potential of AI-powered graph databases!