Case Studies
Jan 4, 2023
Next-generation Intrusion Detection System Based on Graph
Wen Zhou
Qingteng Cloud Security is a host security unicorn company, which focuses on the security of cloud native applications. At present, its main business is the host product named Wanxiang and the container product named Honeycomb. It leads the industry and supports 8 million agents in total. The company's next-generation real-time intrusion detection system based on NebulaGraph and combined with graph technology has been initially put into the market and participated in the 2022 Network Protection, which has achieved good response.
In this topic, we will briefly introduce the intrusion detection system based on graph, hoping to have more people to join in the mining of graph and security application combination.
The status and challenge of intrusion detection
Mainstream intrusion detection system
Intrusion detection has always been a major direction of security research. The two sets of products of Qingteng, Wanxiang and Honeycomb, are host-based and container-based intrusion detection products, both of which have similar principles, as shown below.
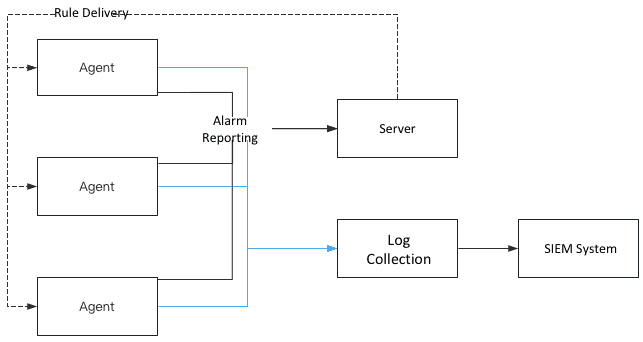
The agent is placed on the host and container side, receiving rules from the server side, combining the collected raw events (process/network connection/file read and write, etc.), and reporting them to the server side as alarms after hitting the rules written by security experts, such as the MD5 of the process file, execution command line, machine learning, and other features. The full amount of raw events are also reported to the server side log collection system and stored in the SIEM system.
Once the alarm is reported to the server, the security staff will take the information related to the alarm to SIEM system to check the events before and after the time of occurrence, log in to the relevant machine to check the relevant information if necessary, and make a comprehensive judgment on whether the current attack alarm is valid and do the relevant disposal.
This system is the current mainstream architecture of intrusion detection, but there are many problems:
For single-point detection based on single events and rules, it may result in false positives due to too loose rules or missed positives due to too strict rules.
Too many alarms may be triggered by the same attack, and security staff have a heavy workload in tracing the source.
The original events related to the same alarm need to be manually analyzed by the SIEM system, which lacks visual means.
The research direction of graph and security
These questions essentially look at each alarm and event independently, when in fact, the alarms and events associated with an attack should be related to each other. We can use graphs to correlate these original events and alarms for overall analysis. In fact, this is also a popular direction of current security research -- traceability graph, with the help of traceability graph we do the following security analysis and detection.
1.Graph detection
Traditional security solutions solve similar IOC detection problems, that is, the judgment of single-point, for the process, network connections, files and other entities is not safe. The actual problem faced by the attack, may not be detected at all points, but the actual behavior is dangerous. A single rule is not fully written, even if the rule can be written, such as hitting a command line, but it will trigger many alarms, and eventually the rule cannot be used. We need to comprehensively judge various combination relationships, which is what graph is good at, and also the problem of graph detection in security. Put all related events into one graph to comprehensively judge whether they are valid attacks.
The research of graph detection started early, but faced with the dual challenges of computational volume and algorithm, the current industry applications are few, and the combined judgments are all in the way of sequence detection. But the sequence rules can not write too many rules in the rule list, otherwise it will lead to the inability to apply the rules. In addition, if the rules are too detailed, and can not be well fuzzy matching rules, it is easy to be bypassed. Hackers can easily bypass these rules with the help of automation tools.
2.Graph association and tracing
Just mentioned alarms, which is another problem all the security products facing today, either the rules do not hit, or too many rule hits, we call this situation alarm flooding. Security staff processing capacity is limited, maybe 100 alarms a day is fine, if a day or even an hour 10000 alarms can not be handled, it is no different from no alarms.
This is really a problem of correlation classification and traceability in security:
An attack will generate a lot of alarms, such as brute force login, used malicious files, executed malicious commands, etc.. The correlation classification to correlate the related alarms in an attack together, which is something the graph is good at. These alarms also allow a comprehensive assessment of whether the current attack is valid or not.
Each alarm will only tell you is a process, file, or network problems, but how this problem occurred, how the hacker came in, where the file was downloaded from, what was done first and then what was done. Security products need to help customers complete this analysis process, the industry is currently with the help of SIEM, THP, SOC and other security products, all the original events are uploaded and saved, and then find security experts, starting from the alarm to check the original event logs, to see what happened before the alarm, which has a relationship may lead to an attack, the process is as short as a few minutes, long as several hours. Security is a confrontation process, early is better, the sooner it is found the sooner it is confronted, blocked or isolated, otherwise it is too late even if it is found. The relevant original event entities (process/network, etc.) can be imported into the graph, with the help of the graph to visually explore and trace the entire attack process, which is the process of graph traceability, academically called causal graph, traceability graph.
3.Graph knowledge mapping and prediction
We know that current security is fundamentally based on rules or a priori knowledge, each vulnerability, Trojan horse, attack tools, attack process, attack organizations have its characteristics, the first few rules are still relatively good description, the attack process and attack organizations are difficult to complete the description.
The current mainstream approach is to build a knowledge base based on security frameworks, the current mainstream has Kill Chain, ATTCK and other frameworks, which is the U.S. Department of Defense-led cyber attack war related to the two companies proposed a security analysis framework, equivalent to the mapping of the tactics and specific attack techniques that delineate the attack. Security academia, such as the University of Illinois and Purdue University have been working on similar issues in the last two years, which is the construction of a security knowledge base (security knowledge mapping). With a complete knowledge base, the ultimate vision of security can be accomplished, for example, if I know your attack process and attack organization, is it possible to stop an attack before it actually starts.
Domestic and international status
At present, the intrusion detection system based on graph that is really taking the lead in the real world is Crowd Strike, a star security company in the U.S. It builds its security system entirely on graphs, which now amounts to doing both graph detection and graph correlation traceability, and is currently valued at 67 billion. Cloud computing giants AWS and Azure are following its approach. Domestic intrusion detection system based on graph, currently there are public information is ThreatBook and Sangfor, they are equivalent to do part of the work of graph correlation and traceability.
Qingteng Cloud Security's Wanxiang and Honeycomb have been working on intrusion detection for many years and have achieved industry-recognized security detection capabilities, so we chose to start with graph association and traceability, and develop a next-generation real-time intrusion detection system based on NebulaGraph combined with graph technology, focusing first on solving the pain point problems of alarm flooding and association traceability.
Qingteng cloud security next-generation intrusion detection system
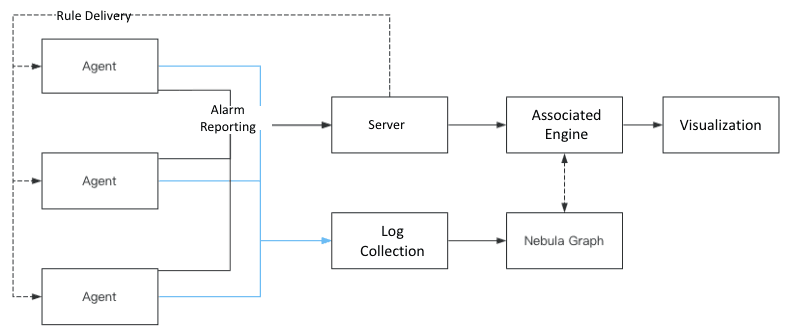
Detection principle architecture diagram
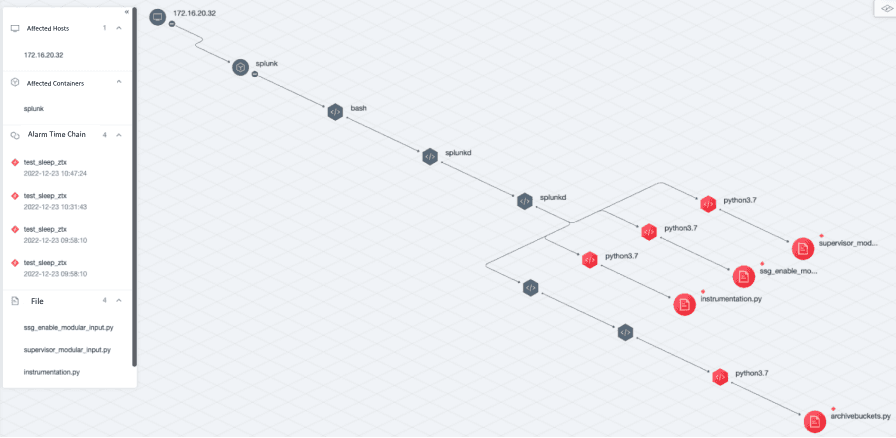
As shown below, the focus is the reported attack alerts and some of the original events are unified and correlated in real time in the graph.
Product effect
The output after correlation processing by the correlation engine is the attack event, an attack event may be associated with multiple attack alerts and visualized, the current product effect is as follows.
The same attack using malicious files and trojans
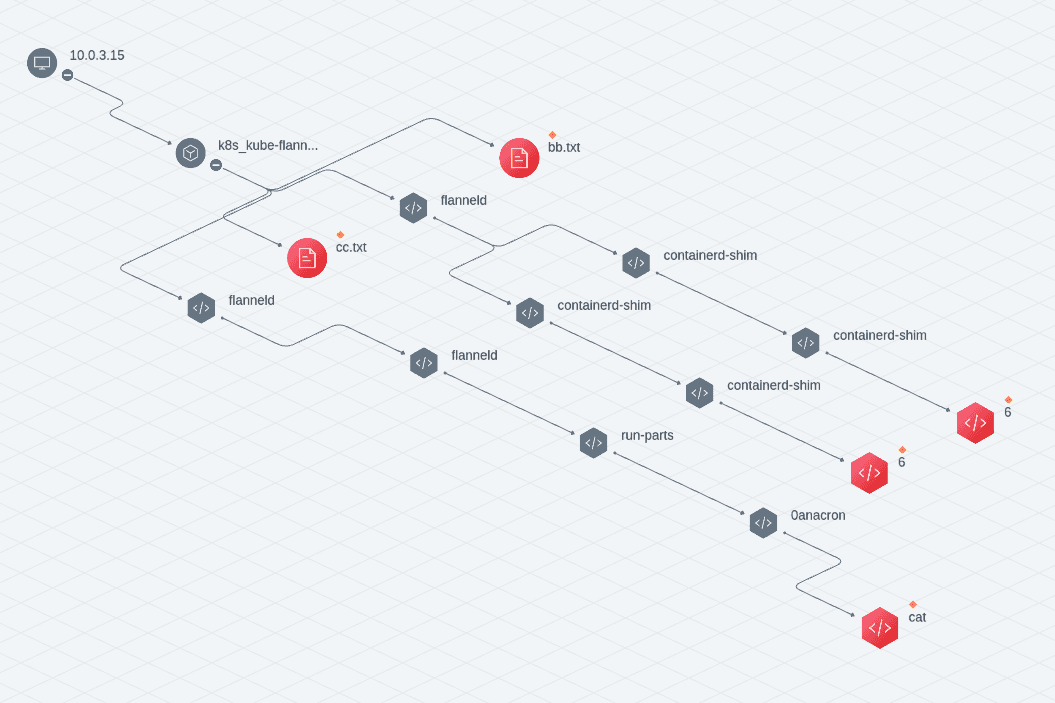
Mounting of sensitive containers
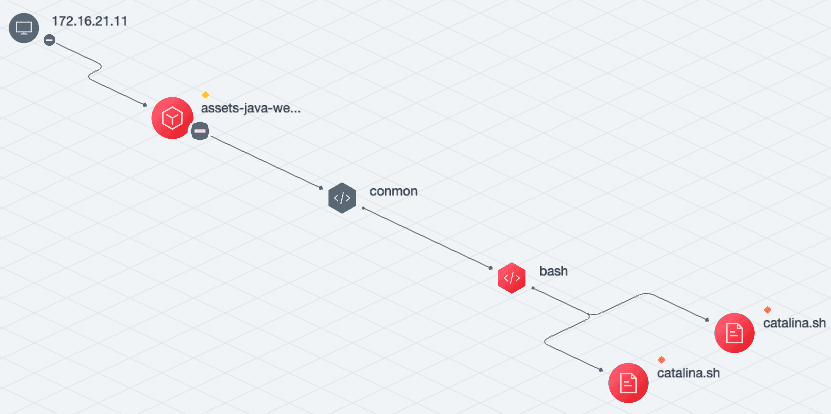
Custom script detection
Advantages of NebulaGraph
NebulaGraph was chosen based on the following considerations.
The immediate need for graph queries, especially for multi-level process relationships during association and traceability. It is much easier to query a graph database with cypher than to query multi-level relationships in a relational database with SQL.
Large-scale storage, involving the storage of a large number of events and alarms.
High-performance query scenarios, associations need to ensure near real-time, the current relevant queries are in ms level.
Thanks to the good performance of NebulaGraph, the association engine enters the graph and calculates the association in a near real-time manner. The tool for importing graph data is the real-time graph entry component created by Qingteng based on Flink, which only needs to change the configuration file to complete the map of points and edges.
Next research direction and plan
At present, the intrusion detection system of Qingteng cloud security mainly supports the association and traceability between single machine and some multi-machine scenarios. The next step is to support more scenarios of multi-machine association with the help of the graph, especially some typical security attack scenarios (rebound/horizontal movement), so as to further enable security with the graph and provide better service for customers.
There are many problems in applying NebulaGraph to graph security applications at present. Some suggestions are given for reference.
1.Push down optimization
In our process of use, the most important problem is the optimization of push down. Such as a diffuse process tree, while specifying the root node and leaf nodes, the order of statement writing may lead to query from the leaf node or the root node, query efficiency varies widely, and finally can only specify the leaf node conditions to force the query from the leaf node.
The performance of MATCH is also essentially a push-down optimization problem, this problem is also encountered a lot, our current approach is to maintain a cache pool for some of the statements have been queried, also note that the official enterprise version actually provides a partial cache function, this point is good if you can consider adding to the community version, is a practical application just need.
2.Some technical requirements for real-time scenarios
Since we are doing real-time association based on NebulaGraph, one of the major problems is how to achieve a balance between consistency and speed, because currently NebulaGraph cannot actually determine whether the graph entry is complete after writing to it. In practice, the association engine needs to poll downstream to determine whether the current vertices and edges is actually in the graph. This problem has some impact on the actual use and performance, and it is worth considering whether there is a better way.
We can see that some competing products, such as TigerGraph and TuGraph, provide the ability to customize the matching and traversal algorithms. In our multi-host association scenario, we have encountered such a need. At present, we can only achieve it by splitting multiple paths and splicing them together. Efficiency and speed are definitely compromised.
3.ToB deployment
Another pain point is the ToB deployment of NebulaGraph. In the security industry, there are still more on-site deployments at home. Especially, state-owned enterprises and government affairs are relatively sensitive to SaaS, so they will face the problem of efficiency and cost.
The first is single-machine deployment. The default production version is a distributed deployment with separate storage and computing designed for the cloud, which is still too cumbersome for ToB deployments and consumes relatively more resources than other databases.
The second is HDD deployment. Considering the cost, many companies, especially small and medium-sized companies, have limited security budgets, which makes it difficult to provide SSD deployment, not to mention the large capacity and high configuration of SSD machines required by the official website. Therefore, more optimization considerations should be made for HDD and low configuration machines.
Above, for Qingteng cloud security team engineer Zhou Wen to share.
Thank you for reading this article.
Want to experience the graph database up close? Now you can use NebulaGraph Cloud on AWS to build your own graph data system, come save a lot of deployment and installation time to get your business done click the link to use the graph database!
If you want to see the source code, you can go to GitHub to read, use, star it -> GitHub. Exchange graph database technology and application skills with other NebulaGraph users, and join "Slack" to play together!

Go From Zero to Graph in Minutes
Spin Up Your NebulaGraph Cluster Instantly!